Nervecentre V9.0 Help for Users
About administering medications
You can administer medications on a desktop and a mobile. For some medications, you might need a witness or counter-signatory.
Depending on your organisation, you can administer medications as part of a drug round.
 About witnessing and countersigning
About witnessing and countersigning
You witness and countersign Approval from a qualified person. For example, a qualified nurse checks and countersigns all medication administered by a student or unregistered health professional. This signature is the Countersign. prescriptions the same way, and can do both with or without scanning.
A secondary check of a medication by a registered professional is called a witness signature. You might need a witness signature for high-risk medications, for example, class 2 medications or IVs. You can enter a witness signature manually or by scanning.
A registered professional must countersign Approval from a qualified person. For example, a qualified nurse checks and countersigns all medication administered by a student or unregistered health professional. This signature is the Countersign. the MAR when a student administers a medication. You can add a countersignature manually or by scanning.
You might need a witness and a countersignature, for example, if a student is administering a controlled medication.
 About single-dose dispensing systems
About single-dose dispensing systems
If your organisation uses a single-dose dispensing system, for example, Optimed, Nervecentre can send prescription information to your single-dose dispensing system. You administer stat and regular medications dispensed by the single-dose dispensing system as part of a drug round. Administer any other medications, for example, PRN medications, dispensed by the single-dose dispensing system, as single medications.
You can only administer a drug round on iOS or a desktop, and not on Android.
Administering medications on a mobile
When administering medications on a mobile, you can use your mobile device's camera, or a wired or Bluetooth scanner that is connected to your mobile device.
 Viewing medications that are due
Viewing medications that are due
There are two ways you can see which medications are due:
-
From your patient list, you can see when medications are due.
-
From your patient list, select a patient, then select Chart.
You can see a list of the patient's medications and when they are due.
You can select a medication from the list to view the prescription timeline. From the prescription timeline, you can administer a dose.
 Overview of the 'five rights'
Overview of the 'five rights'
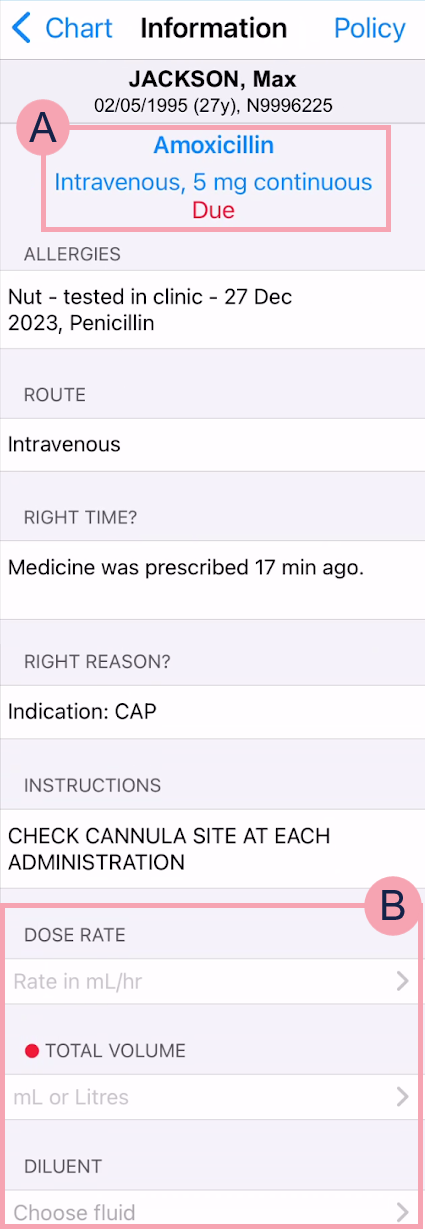
When you administer a medication on a mobile, the 'five rights' screen displays. This is split into two parts.
Read more about administering a medication
Read more about administering fluids and infusions
Part 1:
|
Chart |
Select to return to the list of the patient's medications. |
|
Policy |
Select to view any policies attached to the medication or BNF British National Formulary. The BNF aims to provide prescribers, pharmacists, and other healthcare professionals with sound up-to-date information about the use of medicines. It includes key information on the selection, prescribing, dispensing, and administration of medicines. Medicines generally prescribed in the UK are covered and those considered less suitable for prescribing are clearly identified.. |
|
|
Shows information about the prescription, including the original dose. |
|
ALLERGIES |
Shows the patient's allergies. |
|
ROUTE |
Shows the route for the medication. |
|
THIS DOSE |
If you adjusted the dose, the adjusted dose appears here. |
|
RIGHT TIME? |
|
|
RIGHT REASON? |
Shows a patient's indication, or any associated parameters. For example, blood test results, blood pressure, a change in weight-adjusted dosage, or heart rate. Weight changes display one day after the new weight was recorded. For example, the patient was 63 kg, and today the patient weighs 61 kg. If you administered a medication today, the weight change doesn't display. But if you administer a medication tomorrow, the weight change displays. |
|
INSTRUCTIONS |
Shows any administration instructions added by the prescriber. |
|
|
Select a field to enter information, or select an option. You must complete all mandatory fields. Mandatory fields are marked . |
|
Next |
Appears when all mandatory fields are complete. Select to continue. |
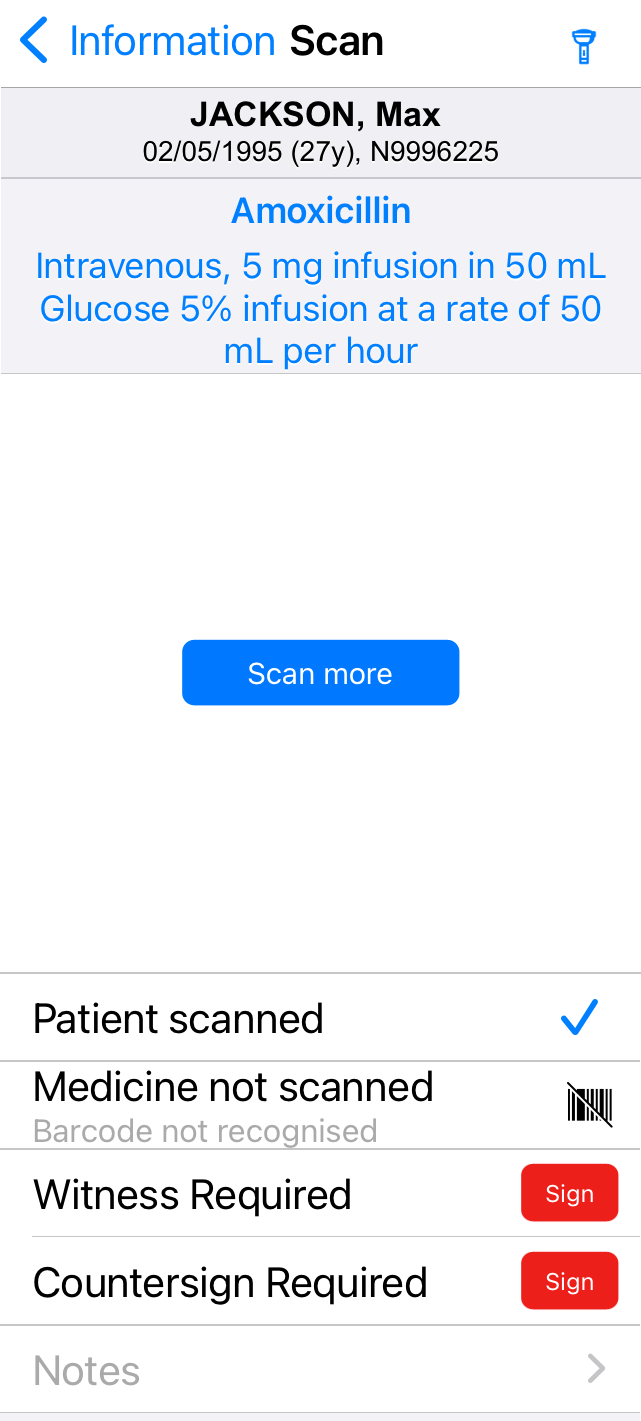
Part 2:
|
|
Select to use your mobile's torch. This can help you when scanning barcodes. |
|
Scan more |
Select to use your mobile's scanner. This only appears on iOS, not on Android. |
|
Patient not scanned |
Scan the patient's wristband. If you can't scan the patient's wristband, select |
|
Patient scanned |
Shows if the patient's wristband has been scanned. |
|
Medicine not scanned |
Scan the medication barcode. If you can't scan the medication barcode, select |
|
Medicine scanned |
Shows if the medication barcode has been scanned. If you need to scan multiple medication barcodes to make a full dose, this shows the number of barcodes you have scanned. |
|
Witness Required |
If a witness is required, this appears. Scan the witness's QR code. If you can't scan their QR code, select Sign and ask them to enter their username and password. |
|
Countersign Required |
If a counter-signatory is required, this appears. Scan the QR code of the counter-signatory. If you can't scan their QR code, select Sign and ask them to enter their username and password. |
|
Notes |
Enter any notes |
|
iOS: Confirm Android: Confirm administered |
This appears after you scan the patient's wristband, the medication barcode, and if required, the QR codes of the witness and counter-signatory. If you are administering a medication, fluid, or infusion, select to confirm it was administered. Read more about administering a medication Read more about administering a fluid or infusion If you are preparing a fluid or infusion, select to confirm it has been prepared but not started. |
|
Prepared |
Only available on Android. This only appears for regular medications, stat doses, and PRNs. This appears after you scan the patient's wristband, the medication barcode, and if required, the QR codes of the witness and counter-signatory. Select to confirm that you prepared the medication, but it has not yet been given to the patient. |
 Accessing your QR code
Accessing your QR code
QR codes change frequently.
If you are witnessing or countersigning a prescription, you can show your QR code to the medication administrator for them to scan, or enter your details on their device.
To access your QR code on iOS:
-
From More, select Settings.
-
Or, from Patients > , select My QR Code.
To access your QR code on Android:
-
From , select Settings.
Administering medications on a desktop
When administering medications on a desktop, you must use a wired or Bluetooth scanner that is connected to your desktop.
 Viewing medications that are due
Viewing medications that are due
There are two ways you can see which medications are due:
-
From Inpatients > Patient List > double-click on a patient's name > Patient Detail, select Clinical.
You can view current medications from Clinical. This is an overview of the MAR.
You can't administer medications from this page.
Read more about the summary of current medications
-
From Inpatients > Patient List > double-click on a patient's name > Patient Detail, select Meds.
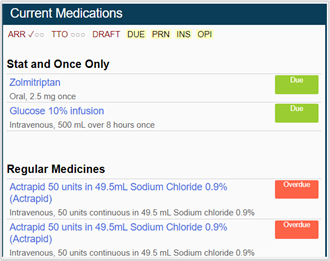
You can view the MAR from Meds. When medications are due, a Due cell is highlighted on the prescription.
Read more about icons on the MAR
You can administer medications from the MAR.
Read more about administering medications
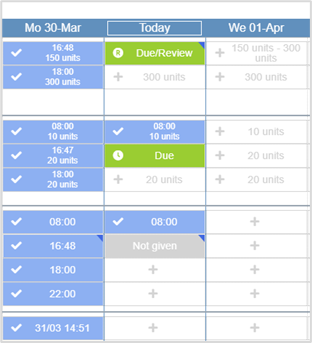
 Icons used on the MAR
Icons used on the MAR
| Detailed view | Compact view | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The medication is due in this time period. |
|
|
|
The drug ‘due’ period has expired. The options available are the same as when the medication is due, meaning it is still possible to give the medication late, or mark it as given retrospectively. |
|
|
|
The drug 'due' period has expired, and the next dose is now due. It is possible to confirm the medication was self-administered, record that the dose was not given, or sign the medication retrospectively. |
|
|
|
The medication was administered at the time shown. { indicates further information has been recorded. Mouseover the cell to view further details. For example, any notes, if the dose has been struck out previously, if the dose was self-administered, or any adverse reactions. You can view more information from the events log. |
|
|
|
The medication has been prepared, but not yet given. |
|
|
|
The infusion has been prepared, but not yet administered. |
|
|
|
The infusion started at the time shown. Mouseover to view the infusion rate, and when the infusion started. |
|
|
|
A dose has not been set for this medication. Depending on your permissions, you can manually set a dose. A dose must be set manually before it can be administered. For example, you might need to set a dose for warfarin. |
|
|
|
When a prescription contains different set doses, the required dose for a specific day or time is shown. |
|
|
|
The variable dose has been adjusted or set. Mouseover the cell to view when the dose was adjusted, who adjusted the dose, and what they changed the dose to. |
|
|
|
The dose has been omitted. Mouseover the cell to view when the dose was omitted, and who omitted the dose. |
|
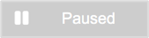
|
|
The prescription was paused for this period. Mouseover the cell to view when the prescription was paused, and who paused the prescription. |
|
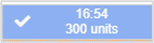
|
|
The set dose has been administered. |
|
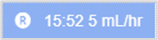
|
|
The rate has been changed. The cell displays the change time and the current infusion rate in mL/hr. Mouseover to view the infusion rate in other units. For example, mg/hr or units/hr. |
|
|
|
The syringe has been changed. The cell displays the change time and the current infusion rate in mL/hr. Mouseover to view the infusion rate in other units. For example, mg/hr or units/hr. |
|
|
|
The infusion is on hold. No further actions can be taken until the infusion has been resumed. Mouseover to view when it was paused, and who paused it. |
|
|
|
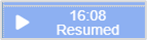
The infusion resumed at the time shown. Mouseover to view when it was resumed, and who resumed it. |
|
|
|
The medication can be administered as needed, and if appropriate. For example, the minimum interval of the medication might prevent you from administering it. |
|
|
|
A PRN Pro Re Nata. It refers to drugs prescribed to be taken as needed, as opposed to at pre-specified intervals. medication has been administered. The number of administrations is shown in the cell. Mouseover to view when the medication was administered, and who administered it. You can also view when and who recorded self-administrations, administrations retrospectively, strikeouts, adverse reactions, and hard reviews. |
|
|
|
Select the cell to place an action on the dose. |
|
|
|
The prescription is or was not active for this period. For example, the start date of the medication might not be shown on your current view. |
|
|
|
The prescription was not given. Mouseover the cell to view when this dose was marked as not given, who marked the dose as not given, and the reason it was not given. |
|
|
|
The dose has been delayed. Administer the dose when the reason for the delay no longer exists. For example, if the delay was because the dose was not available, it should be given when it arrives from the pharmacy. Mouseover the cell to view when the dose was delayed, and who delayed the dose. |
|
|
|
A soft review has been requested (permission based). The medication can be administered as if due, but the review remains until it has been resolved. The review automatically moves to the next dose if not resolved. Mouseover the cell to view when this review was requested, and who requested the review. |
|
|
|
A hard review is needed before the medication can be administered. Mouseover the cell to view when this review was requested, and who requested the review. |
|
|
N/A |
A dose was given retrospectively and needs a witness check. |
 Overview of the 'five rights'
Overview of the 'five rights'
When you administer a medication on a desktop, the 'five rights' screen displays.
Read more about administering a medication
Read more about administering fluids and infusions
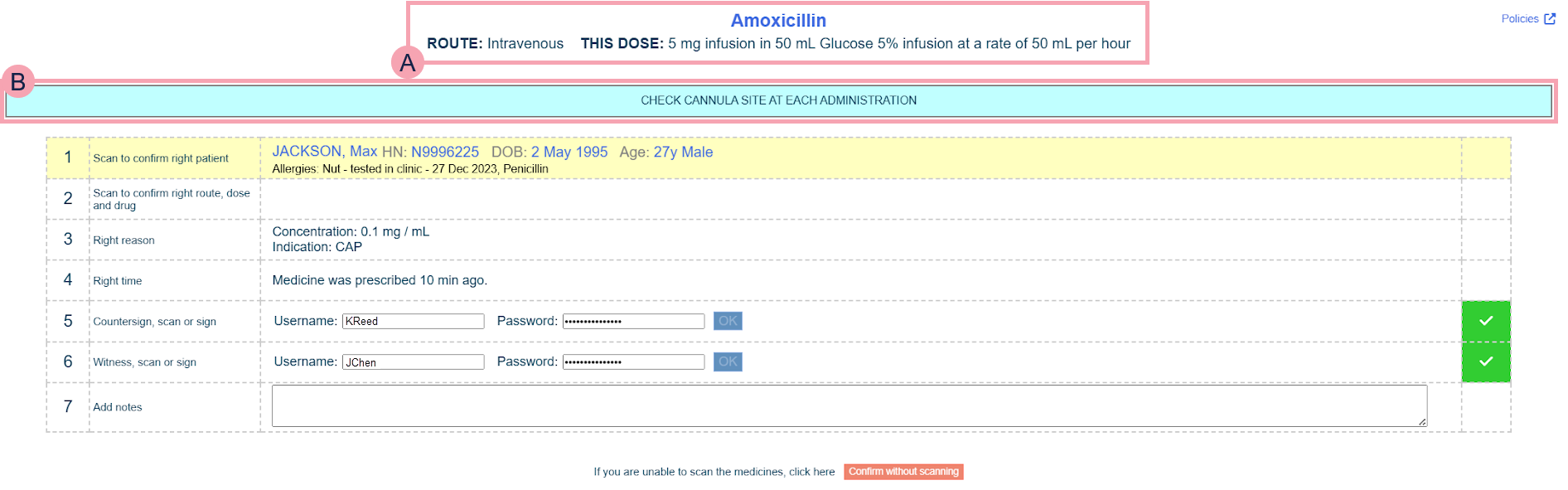
|
|
Shows information about the medication, route, and dose. |
|
Policies |
Select to view any policies attached to the medication. |
|
|
Shows any administration instructions added by the prescriber. |
|
Scan to confirm right patient |
Shows information about the patient, including any allergies recorded. If a patient's allergy matches the medication, Some Allergies Match displays. Scan the patient's wristband to administer the medication. If no scanner is available, or if there is another reason you are unable to scan the patient's wristband, you must positively identify the patient manually. |
|
Scan to confirm right route, dose and drug |
Scan the medication barcode. Information about the scanned medication displays. After scanning the medication barcode, you can:
|
|
Right reason |
Depending on your organisation, this shows a patient's indication, or any associated parameters. For example, blood test results, blood pressure, a change in weight-adjusted dosage, or heart rate. Weight changes display one day after the new weight was recorded. For example, the patient was 63 kg, and today the patient weighs 61 kg. If you administered a medication today, the weight change doesn't display. But if you administer a medication tomorrow, the weight change displays. |
|
Right time |
|
|
Countersign, scan, or sign |
If a counter-signatory is required, this appears. Scan the QR code of the counter-signatory. If you can't scan their QR code, ask them to enter their username and password. |
|
Witness, scan, or sign |
If a witness is required, this appears. Scan the witness's QR code. If you can't scan their QR code, ask them to enter their username and password. |
|
Add notes |
Enter any notes. |
|
Confirm without scanning |
Select this if you can't scan the medication barcode. |
|
Click to confirm given |
This appears after you scan the patient's wristband, the medication barcode, and if required, the QR codes of the witness and counter-signatory. Select to confirm that the medication was administered. |
|
Click to confirm prepared |
This only appears for regular medications, stat doses, and PRNs. This appears after you scan the patient's wristband, the medication barcode, and if required, the QR codes of the witness and counter-signatory. Select to confirm that you prepared the medication, but it has not yet been given to the patient. |
Did you find this article helpful? Yes No
Sorry about that. Our help is a work in progress and we welcome any feedback.
Why wasn't this helpful? Please select one reason:
Great!
Thanks for taking the time to give us some feedback.


 then select a reason.
then select a reason.